Do Varicose Veins Cause Swelling?
One common characteristic of varicose veins is swelling. Learn why this happens and how you can reduce the swelling.

Medically reviewed by Robert T. Fried, MD, on Oct. 7, 2024
If you have varicose veins, you may be concerned about potential complications, even if you’re not experiencing any physical symptoms beyond swollen, achy legs. Many people with spider veins, varicose veins, and other signs of vein disease worry about how these conditions impact blood flow, particularly their risk of developing a blood clot.
While it's essential for blood to clot after an injury, conditions involving vein disease can result in abnormal or problematic blood clotting—even a potentially fatal pulmonary embolism (PE), which occurs when a blood clot gets stuck in the lungs and block blood flow.
Varicose veins don’t directly cause troublesome blood clots, but there’s a definite connection between the two conditions. According to the Cleveland Clinic, severe varicose veins can lead to blood clots, making it crucial to understand exactly how they’re linked. In this blog, we’ll delve into the close connection between varicose veins and blood clots—a critical step to staying proactive about your venous health.
Are you feeling uneasy about your risk of blood clots? We’re here to help. Contact a board-certified physician at Center for Vein Restoration (CVR) for customized treatment that lowers your blood clot risk and results in healthy, beautiful legs.

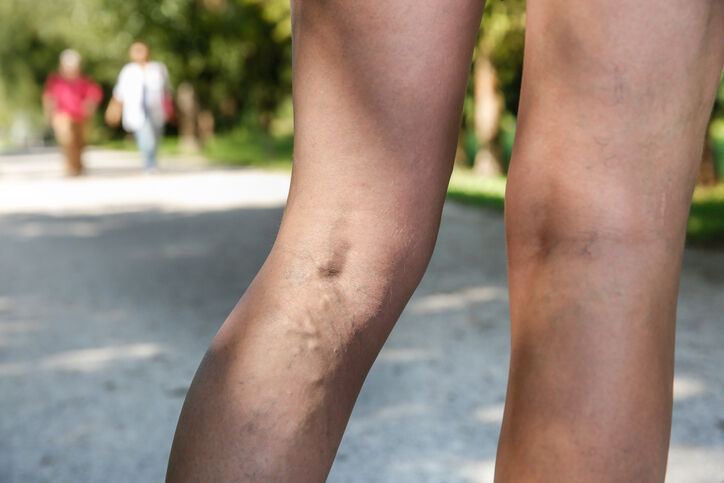
Varicose veins form when leg veins become weakened and damaged. Most leg veins have one-way valves that help blood flow back to the heart. When these valves malfunction, blood begins pooling in the veins. This causes the veins to stretch and become swollen, which creates the visible, bulging veins that we call varicose veins.
Several factors can lead to this problem, such as aging, obesity, genetics, and prolonged sitting or standing. When blood pools in the leg veins, it increases the pressure inside them, making the walls weak and causing them to swell. Pregnancy and hormonal changes can also contribute to the development of varicose veins since these conditions can impact the walls and valves of leg veins.
Varicose veins don’t always show physical symptoms. But, if they become severe enough, they can cause debilitating symptoms such as leg swelling (edema), skin sores (ulcers), itching, thigh cramps (usually at night), and scaly, dry skin. Over time, untreated varicose veins can also cause the skin on the legs and ankles to harden and grow thick, increasing discomfort.
So, what’s the connection between blood clots and varicose veins? Let’s dig deeper.
Unsightly varicose veins without physical symptoms can be covered with clothing or cosmetics. Voilà, problem solved! Blood clots, however, don’t typically have a simple solution, even for short-term relief.
Most blood clots form in superficial veins, or veins that are close to the surface of the skin. This condition, called superficial thrombophlebitis (SVT), means the clot will typically cause the skin to look red as it swells and aches, making its physical and cosmetic symptoms easily discernible.
Meanwhile, a blood clot that forms in a vein deeper in the body—typically in the leg—is called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). This type of clot usually forms because the leg veins are too severely damaged or the blood flow becomes too slow, preventing the body’s natural clotting process from taking place. A DVT can block blood flow in the affected vein, sometimes only partially and other times entirely.
While DVTs most commonly form in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis, they can also develop in other areas such as the arm, intestines, liver, kidneys, or brain, according to the Cleveland Clinic. This is the type of clot that can lead to a PE, a potentially fatal condition that occurs when the clot itself breaks off and becomes stuck deep in the lungs. According to the Mayo Clinic, taking steps to prevent blood clots in the legs helps defend the body from a PE.
This is just one more reason why it’s crucial to seek care immediately if you start to have breathing problems, begin coughing up blood, have chest pain, or have a rapid heartbeat—these could be signs that a PE has developed.
CVR offers a DVT Rule-Out service that delivers prompt, non-invasive testing for deep vein thrombosis (DVT), providing an effective and convenient alternative to emergency room visits.
If you think you or someone you love might have a DVT, call the CVR DVT hotline at 877-SCAN-DVT. This comprehensive service includes scanning, treatment with anticoagulants, education, and follow-up care if necessary.
Now that we’ve discussed the two types of venous blood clots, it’s important to understand how varicose veins can influence the risk of developing them, particularly a DVT, the more dangerous of the two.
The weakened, damaged valves caused by varicose veins can impair blood flow and lead to stagnation, which increases the likelihood of clot formation. When coupled with increased pressure in the veins, this stagnation creates an environment where blood clots are more likely to form. This ultimately means that those with varicose veins are more susceptible to DVTs, which we’ve mentioned can have serious health implications if left untreated.
Knowing how to prevent blood clots can give you a vein health boost moving forward, whether or not you’re currently experiencing signs of vascular disease. Most, if not all, of these prevention methods can also help you improve your overall quality of life. According to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, blood clots can be prevented by:
Ultimately, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution to preventing or treating varicose veins or blood clots. That’s why it’s integral to understand how they’re closely related and achieve relief by seeking personalized care.
If you’re concerned about varicose veins or their risk of causing blood clots, contact CVR today. Our expert team will provide customized treatment plans to address your concerns and help you manage your vein health effectively.
