Medically reviewed by Omonuwa Adah, MD, BSN, on July 11, 2025
Practical Tips for Managing Vein Issues and Protecting Your Leg Health
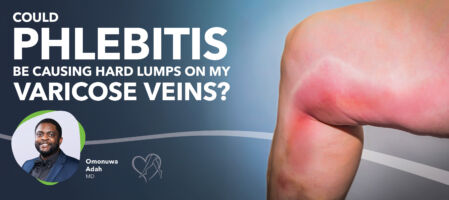
If you’ve noticed a hard, tender lump along a vein in your leg, especially one that’s already enlarged or twisted, you may be experiencing a condition called phlebitis. Phlebitis is the medical term for inflammation of a vein, typically located near the skin's surface.
This inflammation can occur on its own or in conjunction with common vein issues, such as varicose veins or spider veins. When symptoms such as pain, redness, or swelling appear, it may indicate poor circulation in your legs, which can affect your vein health.

Phlebitis can be uncomfortable, and sometimes it is a consequence of a small blood clot in a superficial vein, known as superficial thrombophlebitis. Although not usually dangerous, it can cause pain and should be examined by a qualified vein specialist to exclude more serious issues.
That’s why we consulted with CVR vein expert Omonuwa Adah, MD, BSN, a board-certified vein specialist at Center for Vein Restoration vein clinic in Hamilton, New Jersey, to gain more information about how phlebitis develop, the symptoms to watch for, and the most effective ways to treat and prevent this common, but often overlooked, vein condition.
✅To schedule a consultation with Dr. Adah in Hamilton, New Jersey, CLICK HERE.
✅ Don’t live near Mercer County, New Jersey? Call 240-965-3915 to speak with a helpful Patient Services Representative or schedule your consultation online at one of our 110+ CVR vein clinics near you.
Understanding the difference between everyday vein issues and warning signs of something more serious can help you recognize when to seek expert care, and how to protect yourself and your leg health.
Phlebitis (pronounced flee-bite-iss) is an inflammation of a vein, usually just below the skin. It can occur anywhere in the body, but most often affects the legs. When phlebitis develops in a damaged or weakened vein, such as a varicose vein, it can cause symptoms including a firm, painful lump, warmth, redness, and swelling in the surrounding area.
Phlebitis often occurs in people with vein disease or venous insufficiency, a condition in which the valves in the leg veins don’t function properly, making it harder for blood to flow back to the heart. This can lead to blood pooling in the legs, increasing pressure inside the veins, and raising the risk of inflammation and clotting.
A hard lump on your leg, especially along a visible or bulging vein, can be alarming. As stated previously, in many cases, these lumps are caused by phlebitis, which is inflammation or clotting in a superficial vein.
But phlebitis isn’t the only reason you might notice a lump. Here are some common causes:
Any time you notice a new lump, especially if it’s painful, red, or warm to the touch, it’s best to see a board-certified Center for Vein Restoration (CVR) vein expert. Typically evaluated through a non-invasive venous duplex ultrasound, they can help determine whether the lump is part of a chronic (long-standing) issue, such as venous insufficiency, or something more serious, like deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Call 240-965-3915 to speak with a CVR Patient Services Representative or schedule your consultation online at a CVR near you today.
CVR accepts many insurance providers, including Aetna, Amerigroup, Anthem, Blue Cross/Blue Shield, Cigna, MultiPlan, Medicaid, Medicare, and others.
If you have varicose veins or spider veins, you may already be familiar with symptoms like leg pain, swelling, or a heavy feeling in your legs. However, if a new, hard, and painful lump appears, especially near a vein, it could be a sign of phlebitis.
Here are the most common signs to watch for:
Even though superficial phlebitis isn’t usually dangerous, it can be very uncomfortable, and it sometimes leads to more serious problems if left untreated. In rare cases, a clot in a surface vein can spread into a deeper vein, resulting in deep vein thrombosis.
At Center for Vein Restoration, our board-certified vein specialists are dedicated to helping you feel better, move more freely, and prevent future complications—starting with your very first visit.
📞 Call CVR at 240-965-3915
📅 Or book online HERE
Phlebitis and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) both involve inflammation and blood clots in your veins, but they affect different parts of the body and carry very different levels of risk.
Understanding the difference can help you know when to monitor your symptoms at home and when to seek urgent medical care.
Phlebitis (Superficial Thrombophlebitis):
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT):
A DVT can be dangerous if left untreated, which is why it’s important to take any new or worsening leg symptoms seriously.
If you’re not sure whether your symptoms are due to phlebitis or DVT, don’t wait. A quick, painless ultrasound at a Center for Vein Restoration vein clinic can help provide answers and peace of mind.
💬 Have questions about a lump on your leg or vein symptoms you’re worried about?
📞 Call us today at 877-SCAN-DVT (877-722-6388)
The good news is that phlebitis is usually treatable, and in many cases, symptoms improve with simple at-home care. But it’s still important to see a board-certified vein doctor to make sure your symptoms aren’t caused by something more serious, like a deep vein blood clot.
Treatment for phlebitis depends on the severity of your symptoms and whether a blood clot is present. Your CVR vein specialist will guide you based on your specific situation.

If your symptoms are mild and your doctor has ruled out deep vein thrombosis (DVT), you may be able to manage phlebitis at home with:
Your CVR vein doctor may also recommend light walking or gentle movement to encourage healthy blood flow in your legs.
If phlebitis is persistent, painful, or caused by varicose veins, your CVR vein doctor may recommend a minimally invasive vein treatment to fix the underlying problem. These procedures are done in the office, often with no stitches or downtime, and include:
All of these options are designed to improve circulation, relieve symptoms, and prevent future episodes of phlebitis.
To learn more about your vein health and to discuss if any of these procedures are right for you, schedule an appointment at a Center for Vein Restoration vein clinic near you.

Although phlebitis can be uncomfortable, the steps to help prevent it are simple, and they often aid in addressing other vein issues, such as varicose veins, spider veins, and venous insufficiency.
Whether you’ve had phlebitis before or just want to keep your veins healthy, these habits can make a big difference:
1. Keep Your Legs Moving
Staying active helps your blood flow properly and reduces pressure in your veins. Even light exercise, such as walking, biking, or swimming, strengthens the muscles in your legs and helps prevent blood from pooling.
If you sit or stand for long periods during the day, try to:
2. Wear Compression Stockings
Compression stockings gently squeeze your legs to support healthy blood flow and reduce swelling. They’re especially helpful if you have varicose veins or are recovering from vein treatment.
Ask your Center for Vein Restoration vein specialist if compression therapy is right for you and what level of pressure is recommended for your specific needs.
3. Elevate Your Legs
Lifting your legs above heart level for 15–20 minutes a few times a day can help reduce pressure and swelling in your leg veins, especially after a long day of standing or sitting.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Carrying extra weight puts added pressure on the veins in your legs. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports your overall health and promotes healthy circulation.
5. Stay Hydrated and Limit Salt
Drinking plenty of water keeps your blood flowing well. Too much salt can lead to water retention, which can make leg swelling worse. Choose water or unsweetened drinks and limit salty snacks and processed foods.
6. Avoid Smoking
Smoking damages your blood vessels and slows circulation, increasing your risk for clots and vein disease. If you smoke, talk to your doctor about resources to help you quit. It’s one of the best things you can do for your veins—and your heart.
7. See a Vein Specialist Regularly
Regular check-ins with a CVR vein doctor can catch small issues before they become big problems. If you’ve had phlebitis, varicose veins, or chronic swelling, routine follow-up care can help you stay ahead of symptoms and avoid complications.
Your legs carry you through life. Let CVR help you care for them with expert guidance, real solutions, and compassionate support every step of the way.
📞 Call CVR at 240-965-3915
📅 Or book online HERE
Whether you’re dealing with a hard lump, swollen leg, or want relief from varicose veins, don’t ignore the signs your body is sending. Conditions like phlebitis may seem minor at first, but without proper care, they can lead to more serious problems, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or long-term venous insufficiency.
The good news? You don’t have to manage it alone.
At Center for Vein Restoration (CVR), our board-certified vein specialists are experts in diagnosing and treating all types of vein disease—from spider veins and varicose veins to phlebitis, leg pain, swelling, and more. Using advanced, minimally invasive treatments, we help patients feel better, look better, and get back to living life to the fullest.
With over 110 locations nationwide, CVR makes it easy to find expert vein care near you, without long wait times or hospital stays.
